Singular Value Decomposition
# Tag:
toc test
Singular Value decomposition
- : orthonormal colums, orthonormal basis of
- orthonormal rows, orthonormal basis of
- : diagnal matrix with decreasing order
unique orthonormal basis이지는 않는다. Gram-schmidt를 적용할 때, 를 무엇으로 잡는냐에 따라 달라지듯이, 그 basis는 다양하게 나타날 수 있다.
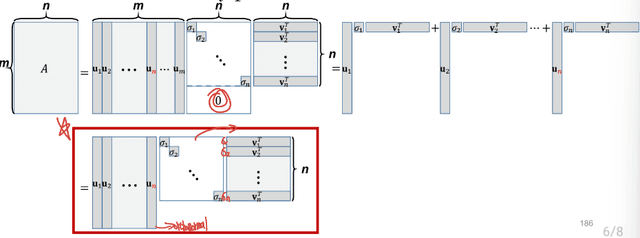
Reduced Form of SVD
See as Eigen decomposition
: : 는 orthonormal columns를 가지므로, 해당 식이 성립한다.
- :: 가 orthonormal 하므로, 에 대해서는 1, 에 대해서는 0이 된다. 일종의 Eigen decomposition을 사용하게 되는 것으로 볼 수 있다.
- Orthogornal eigenvector matrices and : condition of Diagonalization
- Eigenvaleus in that are positive: symmetric matrix라면 always Eigendecomposition이 존재한다. 그리고 이는, SVD와 동일하다.
- Eigenvalues in that are shared by and : and are symmetric positive (semi-) definite.
Spectral Theorem of Symmetric Matrices:
- for square matrix A, : symmetric.
- symmetric matrix: is always orthogonally diagonalizable: 항상 SVD 가능하다.
- eigenspaces are mutually orthogonal, eigenvectors corresponding to different eigenvalues are orthononal: 각기 다른 eigenvalue를 가지게 된다.
Positive Definite Matrices
- positive definite:
- positive semi-definite:

이므로, positive-semi-definite하다. 따라서, Eigenvaluees in 는 모두 positive하다.
Low Rank Approximation
SVD can be represented as sum of outer products:
Approximation of : : : (Frobeneius norm: error값을 제곱해서, 모든 element를 더한 후, 루트를 씌운것이 된다.)
가 된다.
Optimal solution: , 작은 는 무시하게 된다.
Dimension-Reducing transformation
Linear Transformation: ,
m차원을, n차원으로 축소시키는 를 찾는다.
- 는 orthonormal하며, similarity between data items: 를 가장 잘 보존시키는 행렬이 되어야 한다.
- Y의 similarity는, 와 같이 쓰인다.
- Then,
- optimal solution: . when,